Today, scalable product development demands speed, flexibility, and cost efficiency.
However, companies that rely on traditional prototyping cycles often struggle with delays, escalating expenses, and missed market opportunities.
Rapid prototyping addresses these challenges by enabling teams to quickly transform ideas into tangible models, test functionality, and gather feedback early in the process.
For many startups, it also serves as a stepping stone toward building an MVP that can be validated in the real market.
In this guide, we’ll explore the top 10 advantages of rapid prototyping, from reducing costs and accelerating timelines to enhancing innovation and improving collaboration.
What is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is the process of creating quick, iterative models of a product using digital design tools and modern fabrication techniques. The goal is to evaluate concepts, validate designs, and refine features without incurring significant investment in full-scale production.
This makes it especially valuable during the early stages of the MVP development process, where efficiency and learning matter more than perfection.
So unlike traditional approaches that often require months to build a single prototype, rapid prototyping allows teams to move from a digital design to a physical or functional prototype in a matter of hours or days, enabling faster experimentation and reducing the cost of failure.
As a result, this approach allows stakeholders to visualize ideas early, identify usability concerns, and adjust direction long before final manufacturing begins.
Key principles of rapid prototyping include:
- Iteration over perfection – refine designs step by step.
- Early validation – test functionality and gather user input before final development.
- Efficiency – reduce time and cost by focusing on essentials.
By following these principles, organizations can bridge the gap between abstract concepts and working solutions much faster.
Types of Rapid Prototyping Methods
Several methods are commonly used, depending on the stage of product development and desired outcome:
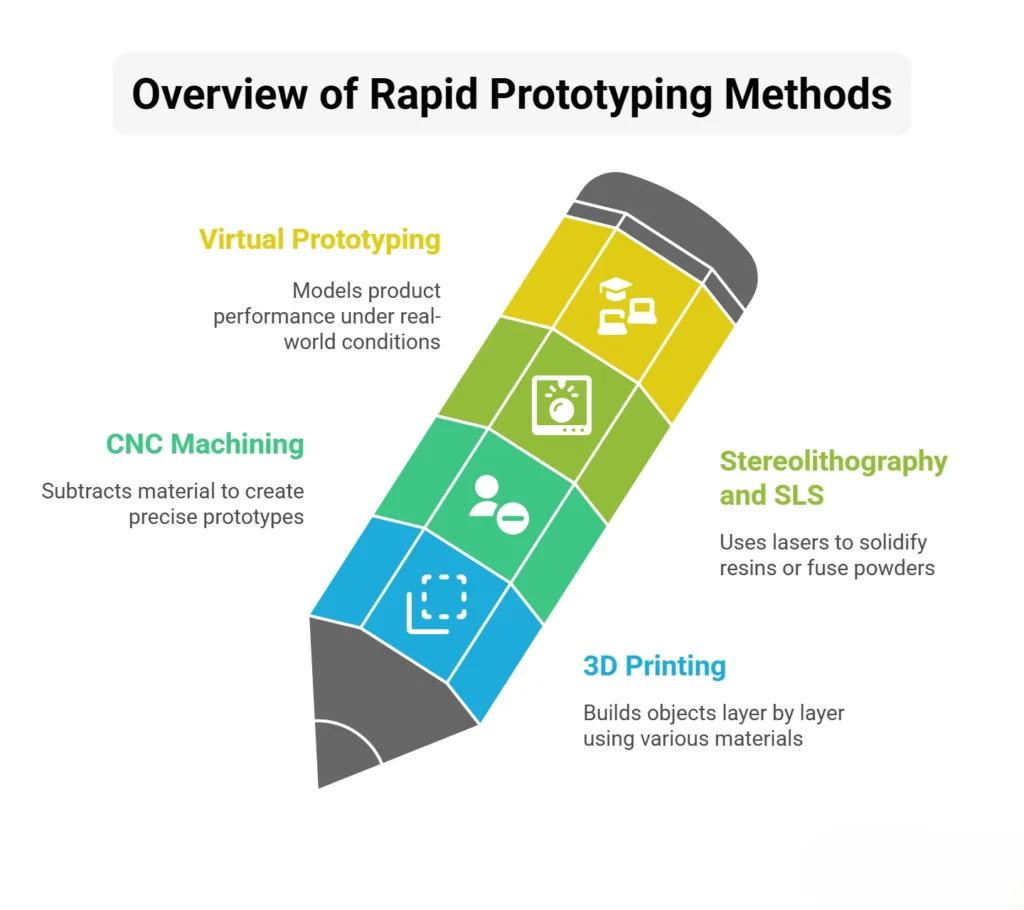
1. 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
One of the most popular rapid prototyping techniques, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer using materials like plastics, resins, or even metals.
It’s ideal for quickly producing physical models of digital designs, enabling teams to test shapes, ergonomics, and basic functionality at a fraction of traditional costs.
2. CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining subtracts material from a solid block to create precise prototypes.
Unlike 3D printing, which is additive, CNC machining is subtractive, making it highly effective for functional prototypes that require durability, accuracy, or testing with production-grade materials.
3. Stereolithography (SLA) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Both SLA and SLS use lasers to solidify liquid resins or fuse powdered materials into solid objects. SLA produces smooth, high-resolution prototypes suited for design validation, while SLS is better for stronger, functional components.
These methods are widely used in industries like automotive and healthcare.
4. Virtual Prototyping and Simulation
Not all rapid prototypes are physical. Virtual prototyping uses CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software and simulation tools to model product performance under real-world conditions.
This method allows teams to test stress, motion, and usability before investing in fabrication, saving significant time and resources.
Each method supports different needs, whether for design validation in rapid prototyping or producing functional prototypes for testing.
Together, they allow businesses to explore designs comprehensively before committing to mass production.
Top 10 Advantages of Rapid Prototyping
The true value of rapid prototyping lies in the measurable benefits it brings to product teams.
Below are ten key advantages that explain why it has become essential in modern product development.
1. Accelerated Product Development Process
Rapid prototyping shortens development cycles by allowing teams to create, test, and refine designs in parallel.
This speed-to-market advantage ensures businesses can respond quickly to changing customer and market needs.
2. Significant Cost Savings on Development
By identifying flaws early and avoiding expensive rework during production, teams achieve rapid prototyping and MVP development cost savings across the entire lifecycle.
Less material waste and fewer design errors also reduce overheads, making the approach more resource-efficient for startups balancing limited budgets.
3. Early Detection and Correction of Design Flaws
Flaws that would otherwise appear late in development can be caught at the prototype stage.
This reduces risk, improves quality, and strengthens product reliability before launch.
4. Enhanced Design Flexibility and Iteration
Designs can be updated and re-tested quickly, encouraging experimentation without heavy investment.
Teams gain freedom to explore multiple variations before finalizing the best option.
5. Improved Stakeholder Communication & Collaboration
Prototypes provide a shared, tangible model that enhances communication among designers, engineers, investors, and clients.
They also help develop clarity in decision-making before committing to building an MVP. Clearer alignment leads to faster approvals and stronger collaboration.
6. Functional Testing and Validation
Functional prototyping enables real-world usability testing to ensure features perform as intended.
It validates technical feasibility while improving confidence in the final product.
7. Customization and Personalization
Prototyping makes it possible to test prototype customization options tailored to specific users or markets.
This approach helps businesses deliver more personalized experiences.
8. Reduced Material Waste & Sustainability
Iterative testing reduces reliance on full-scale production runs, lowering material waste.
This makes rapid prototyping not only cost-efficient but also more environmentally sustainable.
9. Innovation with Complex Designs
If you’ve a technically complex or unconventional product idea, rapid prototyping helps you test without the high risk of failure.
This way, it encourages innovation by making bold concepts practical to explore.
10. Faster Time to Market
Combining speed, efficiency, and early validation, rapid prototyping allows products to move from concept to market-ready versions much faster.
This creates a significant competitive edge.
Disadvantages of Rapid Prototyping
While rapid prototyping offers undeniable advantages, it’s not without limitations. Recognizing these challenges ensures businesses use the approach strategically and avoid overdependence.
Below are some of the most common disadvantages to consider:
1. Higher Costs for Advanced Materials and Methods
Although it saves money overall, rapid prototyping can become expensive if teams rely on advanced 3D printing materials, specialized machinery, or frequent iterations without proper planning.
2. Prototypes May Lack Production-Level Quality
Prototypes often differ from final production models in terms of durability, finish, and performance.
Relying too heavily on early models can create false expectations about the final product.
3. Risk of Over-Iteration
Because it’s so easy to tweak and retest designs, teams may fall into a cycle of endless refinement.
Without clear milestones, this can delay final development and inflate project timelines.
Rapid Prototyping vs. Traditional Prototyping
Understanding how rapid prototyping compares with traditional methods helps teams choose the right approach for their product goals.
| Aspect | Traditional Prototyping | Rapid Prototyping |
| Speed and Efficiency | Often takes weeks or months to produce a single prototype. | Can produce prototypes in hours or days; allows multiple iterations quickly |
| Cost and Resources | High upfront costs for tooling and manufacturing; less resource-efficient. | Lower costs due to reduced tooling and minimized material waste. |
| Iteration and Feedback Cycles | Feedback arrives late, often after significant resources are spent. | Enables early and continuous feedback throughout development. |
| Complexity and Innovation Support | Limited in handling complex or unconventional designs; costly to experiment with.. | Supports complex geometries and innovative designs affordably. |
Conclusion
Rapid prototyping largely empowers teams to accelerate iterations, cut costs, and encourage collaboration. It helps them validate ideas quickly and with greater confidence.
While challenges like material limitations or upfront equipment investments exist, the advantages far outweigh the drawbacks.
For startups, rapid prototyping is often the bridge between early-stage concepts and a market-ready MVP. At American Chase, we help businesses bridge that gap, ensuring prototyping aligns with your broader innovation strategy.
By adopting the right methods and aligning them with your development strategy, you can move from concept to launch with greater efficiency and success.
Contact our experts today.
FAQs
1. What is rapid prototyping, and how does it differ from traditional prototyping?
Rapid prototyping uses modern digital design and fabrication tools like 3D printing or CNC machining to create quick, iterative models, whereas traditional prototyping often takes longer and requires higher costs for tooling and setup.
2. What are the main advantages of using rapid prototyping in product development?
The key advantages include faster design iterations, reduced development costs, improved stakeholder collaboration, and the ability to test functionality early in the process.
3. How does rapid prototyping impact innovation and customization?
It allows teams to experiment with complex geometries and personalized designs without incurring significant costs, fostering innovation while meeting unique customer needs.
4. How does rapid prototyping reduce costs and time-to-market?
By avoiding full-scale production early on, teams save on material and tooling expenses while shortening development cycles, which accelerates speed-to-market.
5. Can rapid prototyping be used for functional and user testing?
Yes, advanced methods like CNC machining and SLS produce durable, functional prototypes that can undergo real-world testing before mass production.
6. What industries benefit most from rapid prototyping?
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, healthcare, and manufacturing rely heavily on rapid prototyping to test designs, reduce risk, and innovate faster.
7. What are common challenges when adopting rapid prototyping techniques?
Challenges include limited access to advanced materials, initial equipment costs, and ensuring digital design accuracy. These can be overcome by choosing the right prototyping method and integrating it early into product development.