Successful SAP implementation has become a critical factor for organizations seeking digital transformation and operational excellence.
SAP provides enterprises with integrated solutions to streamline processes, enhance productivity, and drive growth.
As we navigate through 2025, the approach to SAP continues to evolve with emerging technologies and methodologies.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through every aspect of SAP implementation, from initial planning to post-implementation optimization. This ultimately ensures your project delivers maximum value and minimal disruption.
What is SAP Implementation?
SAP refers to the complex process of deploying, configuring, and integrating SAP software systems within an organization’s existing infrastructure. Understanding the fundamentals of SAP implementation is essential for project success and achieving desired business outcomes.
Definition and Overview
SAP involves the systematic process of installing, configuring, and customizing SAP software solutions to align with an organization’s business processes and requirements.
Moreover, successful SAP implementation requires careful planning, strategic execution, and ongoing maintenance to ensure optimal performance and user adoption.
SAP vs Traditional ERP Systems
For instance, SAP offers more robust integration capabilities, allowing for seamless data flow across departments and functions.
Additionally, SAP’s modular structure provides greater flexibility, enabling organizations to implement only the components they need.
According to a 2024 Gartner report, organizations implementing SAP solutions experience 27% higher integration success rates compared to traditional ERP systems.
In contrast to legacy systems, SAP implementation delivers more comprehensive analytics and reporting capabilities, enabling data-driven decision-making throughout the organization.
Key SAP Modules and Applications
Specifically, SAP Financial Accounting (FI) and Controlling (CO) form the backbone of financial operations, providing comprehensive tools for budget management, cost accounting, and financial reporting.
Meanwhile, SAP Human Capital Management (HCM) streamlines HR processes, from recruitment to retirement, enhancing employee experience and operational efficiency.
Furthermore, SAP Materials Management (MM) and Production Planning (PP) optimize supply chain operations, inventory management, and manufacturing processes.
In addition, SAP Sales and Distribution (SD) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) improve customer engagement, sales processes, and service delivery. Consequently, understanding these core modules is essential for effective SAP implementation planning and execution.
Benefits of SAP Implementation in 2025
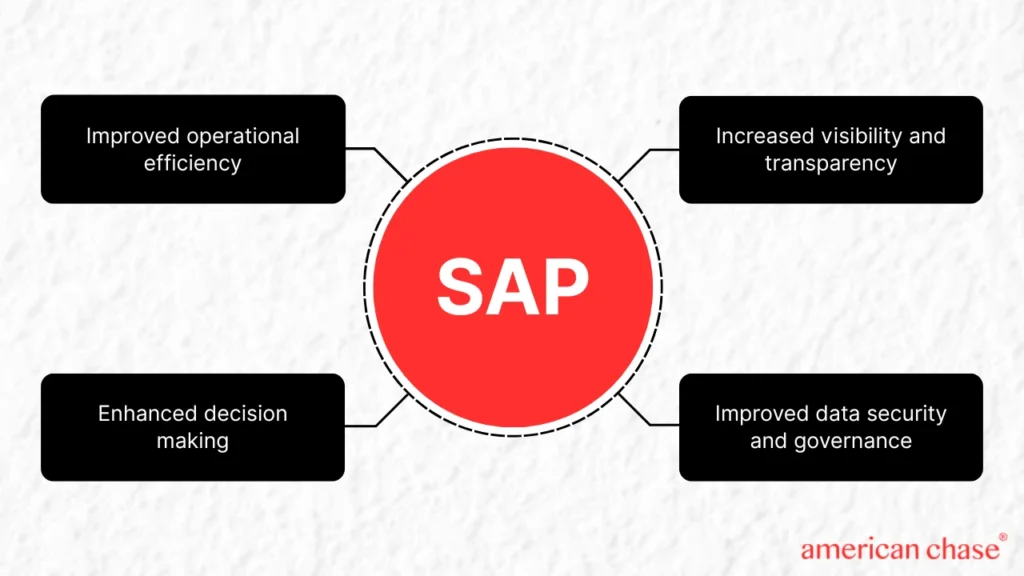
Successful SAP implementation delivers transformative benefits across all business dimensions. Understanding these advantages helps organizations build compelling business cases and set realistic expectations for their SAP projects.
1. Improved Operational Efficiency
SAP implementation significantly enhances operational efficiency by standardizing and automating business processes across the enterprise.
As a result, organizations experience streamlined workflows, reduced manual interventions, and accelerated process execution.
Additionally, SAP’s integrated architecture eliminates data silos, enabling seamless information flow between departments and functions. Consequently, this integration reduces duplicate efforts, minimizes errors, and ensures process consistency, creating a foundation for continuous operational improvement.
2. Enhanced Decision Making with Real-Time Data
Effective SAP implementation transforms decision-making capabilities by providing real-time access to critical business data and insights. For instance, executives and managers can access dashboards and reports showing current performance metrics, enabling prompt corrective actions when needed.
Furthermore, SAP’s advanced analytics capabilities turn raw data into actionable insights, supporting strategic planning and tactical decision-making. Therefore, this enhanced visibility and analytical power drive more informed, timely, and effective business decisions.
3. Increased Visibility and Transparency
SAP implementation delivers unprecedented visibility and transparency across organizational operations, breaking down traditional information barriers. This improved visibility fosters greater accountability, facilitates more effective resource allocation, and enables proactive problem identification and resolution.
- First, comprehensive tracking and monitoring capabilities enable real-time status updates on orders, inventory, production, and financials.
- Second, enhanced audit trails and documentation improve compliance and governance, reducing regulatory risks.
- Third, centralized data repositories ensure consistent information across the organization, eliminating discrepancies and confusion.
4. Improved Data Security and Governance
Modern SAP implementation provides robust security features and governance frameworks to protect sensitive business information. Specifically, role-based access controls ensure users can only access information relevant to their responsibilities, reducing data exposure risks.
Additionally, SAP’s advanced encryption and authentication mechanisms protect data at rest and in transit from unauthorized access. Furthermore, comprehensive audit trails and monitoring capabilities enable security teams to detect and respond to potential threats promptly.
5. ROI and Cost Savings
Strategic SAP implementation delivers substantial return on investment through multiple cost-saving mechanisms. Initially, process automation reduces labor costs and improves resource utilization across functions.
Subsequently, improved inventory management and supply chain optimization minimize carrying costs and waste. Furthermore, enhanced financial controls and visibility reduce revenue leakage and improve cash flow management.
Additionally, standardized processes and centralized data management reduce IT maintenance and support costs. Consequently, these combined benefits create a compelling financial justification for SAP investment.
Pre-Implementation Requirements
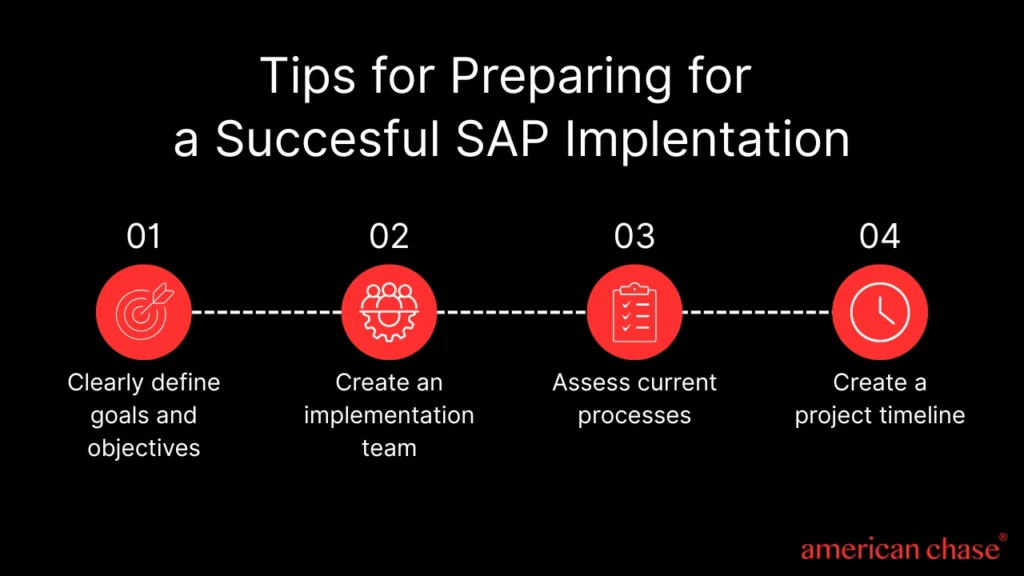
Before embarking on an SAP implementation journey, organizations must address several critical prerequisites to ensure project success and minimize disruption.
A thorough organizational readiness assessment forms the foundation of successful SAP by identifying potential gaps and challenges early in the process.
1. Organizational Readiness Assessment
First, this assessment evaluates current business processes against SAP best practices, highlighting areas requiring redesign or adaptation. Second, it examines organizational structure and governance models to ensure alignment with SAP implementation requirements.
Third, it assesses the organization’s change management capabilities and cultural readiness for transformation. Consequently, this comprehensive evaluation helps develop targeted strategies to address identified gaps and prepare the organization for successful SAP adoption.
2. IT Infrastructure Evaluation
Rigorous IT infrastructure evaluation ensures the technical foundation can support SAP implementation requirements and performance expectations.
Additionally, it identifies potential integration points with existing systems and evaluates compatibility challenges. Furthermore, it assesses current security protocols and infrastructure against SAP’s security requirements and best practices.
Therefore, this detailed evaluation helps organizations develop infrastructure upgrade plans and address technical constraints before beginning SAP.
3. Budget Planning and Cost Considerations
Comprehensive budget planning is essential for successful SAP, encompassing both obvious and hidden cost elements. Initially, organizations must account for software licensing, hardware upgrades, and implementation consulting services.
Subsequently, they should budget for data migration, system integration, and customization requirements. Furthermore, allocations for training, change management, and post-implementation support are crucial for long-term success.
Consequently, this thorough financial planning helps secure appropriate funding and manage stakeholder expectations throughout the implementation journey.
4. Resource Allocation and Team Building
Strategic resource allocation and team building create the human foundation for successful SAP implementation. As a result, organizations must identify and secure both internal subject matter experts and external implementation partners with the right skills and experience.
Additionally, a well-structured implementation team should include representatives from all affected business units to ensure comprehensive requirements gathering and buy-in.
SAP Implementation Methodologies
Selecting the appropriate implementation methodology significantly impacts project timeline, cost, and success rate. Understanding available approaches helps organizations make informed decisions aligned with their specific needs and constraints.
1. ASAP Methodology Overview
The Accelerated SAP (ASAP) methodology provides a structured framework specifically designed for efficient SAP implementation.
Firstly, this proven approach divides the implementation process into five distinct phases: project preparation, business blueprint, realization, final preparation, and go-live and support.
Moreover, each phase includes specific deliverables, milestones, and quality gates to ensure comprehensive coverage and risk management.
Furthermore, the ASAP methodology incorporates accelerators, templates, and tools to streamline implementation activities and promote standardization.
Consequently, this structured approach reduces implementation time, enhances quality, and improves predictability for organizations undertaking SAP projects.
2. Agile vs Waterfall Approaches
When comparing implementation methodologies for SAP implementation, the choice between agile and waterfall approaches presents significant trade-offs and considerations.
In the traditional waterfall model, implementation progresses sequentially through distinct phases, providing clear documentation and predictability.
Conversely, agile SAP implementation employs iterative cycles, delivering functional components in sprints while allowing for adjustments based on feedback.
According to a 2024 Project Management Institute study, agile SAP completes 28% faster on average but requires more intensive stakeholder engagement.
3. Hybrid Implementation Models
Hybrid implementation models combine elements of various methodologies to create tailored approaches for SAP implementation that address specific organizational needs and constraints.
For instance, these models might utilize the structured documentation of waterfall methods for core financial modules while applying agile techniques for customer-facing components.
Additionally, hybrid approaches typically incorporate phased rollouts based on business priorities and interdependencies. Consequently, this flexible approach allows organizations to balance structure and adaptability, potentially delivering faster time-to-value while managing implementation risks.
7 Key Stages of SAP Implementation
Successful SAP implementation follows a structured process with distinct stages, each building upon the previous one to ensure comprehensive coverage and risk management.
The project preparation and planning stage establishes the foundation for successful SAP by defining the scope, assembling resources, and creating the project framework.
Stage 1: Project Preparation and Planning
During the first critical stage, organizations conduct thorough requirements gathering through workshops and interviews with key stakeholders across business units.
Additionally, project teams develop detailed scope definitions, establishing clear boundaries and deliverables for the implementation effort. Consequently, this stage culminates in creating comprehensive timelines with defined milestones that will guide the entire SAP journey.
Stage 2: Business Blueprint
The business blueprint stage documents current processes and designs future state operations for SAP implementation, creating the detailed roadmap for system configuration.
First, implementation teams conduct current process documentation through workshops and interviews, capturing existing workflows, systems, and pain points
.Second, comprehensive gap analysis identifies differences between current operations and SAP best practices, highlighting areas requiring customization or process redesign.
Third, future state design workshops develop detailed process maps showing how operations will function after SAP implementation. Consequently, these activities produce customization requirements documentation, specifying the system adaptations needed to support business requirements.
Stage 3: Realization/Configuration
During the realization and configuration stage, the conceptual blueprint transforms into a functional SAP implementation system through systematic development and integration activities.
Specifically, system configuration involves setting up organizational structures, master data elements, and business rules according to the approved blueprint.
Meanwhile, change management planning intensifies, developing communication strategies, training materials, and transition plans to prepare the organization for the upcoming transformation.
Stage 4: Testing Phase
The testing phase verifies system functionality and performance before SAP implementation goes live, identifying and resolving issues in a controlled environment. Initially, unit testing examines individual components and transactions to ensure they perform as specified in isolation.
Subsequently, integration testing evaluates how these components work together across business processes and system boundaries. Furthermore, user acceptance testing involves business representatives validating that the system meets their requirements and supports their daily activities.
Additionally, performance testing assesses system responsiveness, scalability, and stability under expected and peak load conditions.
Stage 5: Final Preparation
The final preparation stage ensures operational readiness for SAP implementation by addressing people, data, and infrastructure requirements.
During this critical phase, organizations conduct comprehensive end-user training through various methods, including classroom sessions, online modules, and hands-on workshops.
Additionally, data migration planning finalizes extraction, transformation, and loading procedures for transferring historical data into the new SAP environment.
Stage 6: Go-Live
The go-live stage represents the culmination of the SAP implementation journey, transitioning the system from preparation to productive operation.
- First, production deployment activates the configured SAP environment, making it available for business operations.
- Second, data migration execution transfers cleansed historical data from legacy systems into the new SAP environment according to the established migration plan.
- Third, system monitoring begins, with technical teams closely observing performance metrics, error logs, and user activities to identify potential issues. Consequently, issue resolution processes are activated to address any problems that emerge, ensuring business continuity during this critical transition period.
Stage 7: Post-Implementation Support
The post-implementation support stage ensures the long-term success of SAP implementation through continuous improvement and responsive assistance.
Initially, ongoing maintenance activities address system issues, apply patches, and implement enhancements to maintain optimal performance. Subsequently, performance optimization efforts analyze system behavior and user feedback to identify and resolve bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
Furthermore, user support services assist help desks, knowledge bases, and subject matter experts to resolve operational questions and issues.
Common SAP Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Despite careful planning, SAP implementation projects often face challenges that can impact timeline, budget, and outcomes. Understanding these common obstacles and their solutions helps organizations prepare effective mitigation strategies.
1. Budget Overruns
Budget overruns represent one of the most common challenges in SAP projects, often derailing otherwise successful initiatives. According to a 2024 KPMG survey, 62% of SAP implementation projects exceed their initial budgets by an average of 27%.
To address this challenge, organizations should implement detailed cost-tracking systems that monitor expenditures against budget allocations in real-time. Additionally, establishing a formal change management process helps contain scope creep that often drives unexpected costs.
Furthermore, creating contingency reserves of the total budget provides a buffer for unforeseen challenges. Consequently, combining these approaches helps maintain financial control throughout the SAP journey.
2. Timeline Delays
Timeline delays during SAP implementation can disrupt business operations and erode stakeholder confidence in the project. For instance, resource constraints, scope expansion, and technical challenges frequently extend project timelines beyond initial estimates.
To mitigate these risks, implementation teams should develop detailed project schedules with realistic timelines that include buffer periods for unexpected issues.
3. Resistance to Change
Resistance to change presents a significant obstacle to successful SAP implementation, potentially undermining even technically flawless deployments.
As a result, organizations must develop comprehensive change management strategies that address both rational and emotional aspects of user resistance.
Additionally, early stakeholder engagement through workshops, focus groups, and preview sessions builds awareness and buy-in throughout the organization.
4. Technical Complexities
Technical complexities frequently arise during SAP implementation, particularly when integrating with legacy systems or addressing unique business requirements. Specifically, data migration challenges, interface issues, and performance problems can significantly impact implementation timelines and outcomes.
To address these challenges, organizations should conduct thorough technical feasibility assessments during the planning phase to identify potential issues early.
Additionally, establishing a dedicated technical team with specialized expertise in SAP architecture and integration helps resolve complex issues efficiently. Therefore, these proactive measures help navigate technical complexities and ensure a stable, high-performing SAP environment.
5. Integration Issues
Integration issues often emerge as critical challenges during SAP implementation, particularly in organizations with complex system landscapes and numerous interfaces. For instance, incompatible data formats, asynchronous processing requirements, and legacy system limitations can create significant integration hurdles.
To overcome these challenges, implementation teams should develop detailed integration maps documenting all system connections, data flows, and processing requirements.
SAP Implementation Best Practices for 2025
Adhering to proven best practices significantly increases the success rate of SAP projects while reducing risks and optimizing outcomes. The decision between cloud and on-premise deployment represents a fundamental strategic choice in SAP implementation planning.
1. Cloud vs On-Premise Considerations
First, Cloud & DevOps integrations typically offer faster deployment, reduced infrastructure costs, and automatic updates, but may provide less customization flexibility.
Second, on-premise deployments deliver greater control over system configurations, security implementations, and upgrade timing but require significant infrastructure investments and maintenance resources.
Therefore, organizations must carefully evaluate their specific requirements, security needs, and long-term strategic objectives when making this critical deployment decision.
2. Industry-Specific Requirements
Addressing industry-specific requirements during SAP implementation ensures the solution delivers maximum value and competitive advantage. Specifically, manufacturing companies should focus on production planning, shop floor control, and quality management capabilities during implementation.
Meanwhile, retail organizations typically prioritize inventory management, point-of-sale integration, and customer experience functionalities. Furthermore, financial services firms emphasize regulatory compliance, risk management, and financial reporting features in their SAP implementations.
3. Security and Compliance
Robust security and compliance frameworks are essential components of successful SAP implementation, protecting sensitive business data and ensuring regulatory adherence.
Initially, implementation teams should conduct comprehensive security assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and compliance requirements.
Additionally, compliance-specific configurations and reports should be implemented to support regulatory requirements like GDPR, SOX, and industry-specific regulations.
4. Mobile and AI Integration
Modern SAP implementation increasingly incorporates mobile capabilities and AI technologies to enhance user experience and operational efficiency.
For instance, mobile-enabled SAP applications allow employees to access critical information and perform key transactions from anywhere, improving productivity and response times.
Furthermore, intelligent automation technologies streamline routine processes, reducing manual effort and error rates. Consequently, these advanced technologies transform SAP implementation from transaction processing systems to intelligent business platforms.
Choosing the Right SAP Implementation Partner
Selecting the appropriate implementation partner significantly impacts project success, timeline, and overall outcomes. A thoughtful selection process helps organizations find partners aligned with their specific needs and objectives.
1. Evaluation Criteria
Establishing comprehensive evaluation criteria ensures organizations select optimal partners for their SAP implementation journey.
First, technical expertise assessment should examine the partner’s experience with specific SAP modules, integration capabilities, and technical certifications.
Second, industry knowledge evaluation should verify the partner’s understanding of sector-specific processes, regulations, and best practices.
Third, the project methodology review should assess the partner’s implementation approach, tools, and accelerators to ensure alignment with organizational preferences.
Consequently, this structured evaluation process helps identify partners best positioned to deliver successful SAP implementation outcomes.
2. In-House vs External Partners
The decision between in-house implementation and external partners represents a strategic choice with significant implications for SAP success.
Specifically, in-house teams offer deeper organizational knowledge and potentially greater control but may lack specialized SAP expertise and implementation experience.
Conversely, external partners bring broader implementation expertise and best practices but require more effort to understand organizational culture and unique requirements.
3. Third-Party Support Options
Diverse third-party support options complement primary implementation partners, providing specialized expertise for specific aspects of SAP. For instance, specialized data migration partners offer advanced tools and methodologies for complex data transfers from legacy systems.
Additionally, testing automation specialists provide frameworks and tools to accelerate validation processes and improve test coverage. Furthermore, change management consultants bring proven methodologies for addressing the human aspects of SAP implementation.
4. Partner Certifications and Experience
Partner certifications and experience provide objective measures for evaluating potential SAP implementation collaborators. Initially, organizations should verify SAP partnership levels, which indicate the partner’s investment in SAP expertise and commitment to quality standards.
Subsequently, reviewing specific module certifications ensures the partner possesses validated expertise in relevant functional areas. Therefore, these objective credentials help organizations make informed decisions when selecting implementation partners.
SAP Implementation Timeline and Costs
Understanding typical timelines and cost structures helps organizations set realistic expectations and develop accurate budgets for their SAP projects. SAP implementation timelines vary significantly based on scope, complexity, and organizational factors.
1. Typical Project Durations
For small to medium implementations focusing on core modules, typical durations range from 6-12 months from planning to go-live. Meanwhile, comprehensive enterprise-wide implementations involving multiple modules and locations typically require 12-24 months for full deployment.
Consequently, organizations should develop realistic timelines considering their specific scope, resource availability, and desired implementation approach.
2. Cost Breakdown and Factors
Understanding cost breakdown and influencing factors enables more accurate budgeting for SAP implementation projects.
Specifically, software licensing typically represents 20-30% of total implementation costs, varying based on modules selected and user counts. Additionally, implementation services, including configuration, customization, and project management, generally account for 30-40% of the budget.
Furthermore, hardware and infrastructure investments contribute to on-premise deployments but are minimal for cloud implementations.
3. Hidden Costs to Consider
Beyond obvious expenses, SAP implementation projects often incur hidden costs that can significantly impact total investment. Furthermore, productivity losses during transition periods represent real but often uncalculated costs as users adapt to new systems and processes.
- First, change management activities, including communication, training, and user adoption efforts, typically require 8-12% of the total budget but are frequently underestimated.
- Second, data cleansing and migration efforts often consume 5-10% of project resources, particularly in organizations with fragmented or inconsistent data sources.
- Third, post-implementation support and stabilization typically require 10-15% of the initial project budget during the first year after go-live. Therefore, comprehensive budget planning should account for these hidden costs to ensure adequate funding throughout the implementation journey.
4. ROI Timeline Expectations
Establishing realistic ROI timeline expectations helps manage stakeholder perceptions and maintain support throughout the SAP implementation process.
Initially, organizations typically experience decreased productivity during implementation and the immediate post-go-live period as users adapt to new systems and processes.
Subsequently, operational improvements begin emerging 3-6 months after implementation as processes stabilize and users become proficient.
Furthermore, strategic benefits typically materialize 9-18 months after implementation as organizations leverage enhanced data and capabilities for competitive advantage.
Post-Implementation Optimization
The journey doesn’t end with go-live; ongoing optimization ensures organizations maximize the value of their SAP investment over time. Effective continuous improvement strategies transform SAP implementation from a one-time project to an evolving business capability.
1. Continuous Improvement Strategies
Initially, establishing a center of excellence provides dedicated resources for ongoing system optimization and enhancement. Subsequently, implementing regular process reviews identifies opportunities for further automation and streamlining.
Furthermore, gathering user feedback through surveys and focus groups highlights pain points and improvement opportunities from the frontline perspective. Additionally, benchmarking performance against industry standards helps identify areas where the organization lags behind best practices.
2. Performance Monitoring
Comprehensive performance monitoring ensures SAP implementation continues to meet business needs while identifying optimization opportunities. Specifically, technical monitoring tracks system response times, resource utilization, and error rates to identify performance bottlenecks and stability issues.
Additionally, process monitoring measures transaction throughput, completion times, and exception rates to evaluate operational efficiency.
Therefore, this multi-dimensional monitoring approach provides a holistic view of system performance, enabling targeted optimization efforts that deliver maximum business value.
3. System Updates and Upgrades
Strategic management of system updates and upgrades ensures SAP implementation remains current while minimizing business disruption. For instance, establishing a regular patching schedule helps maintain system security and stability without overwhelming support resources.
Additionally, developing a long-term upgrade roadmap aligned with business priorities ensures the organization gains access to new capabilities when they deliver maximum value.
Furthermore, implementing structured testing protocols for updates minimizes the risk of business disruption from unexpected issues. Consequently, this systematic approach to system maintenance balances the benefits of new capabilities against the costs and risks of implementation changes.
4. User Adoption Tracking
User adoption tracking provides critical insights into the effectiveness of SAP implementation and identifies areas requiring additional support or optimization.
- First, usage analytics monitor transaction volumes, feature utilization, and user engagement patterns to identify adoption gaps.
- Second, error tracking identifies common mistakes and workflow challenges that may indicate training needs or usability issues.
- Third, efficiency metrics measure time-to-completion for key processes compared to baseline measurements, highlighting productivity impacts. Therefore, these comprehensive tracking mechanisms provide valuable feedback for continuous improvement initiatives.
Conclusion
Successful SAP implementation represents a transformative journey that delivers significant business value when executed effectively. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the essential components of SAP implementation, from initial planning through post-implementation optimization.
Remember that SAP implementation is not merely a technical project but a business transformation initiative requiring careful attention to people, processes, and technology aspects.
As SAP technologies continue evolving, we at American Chase stay informed about new capabilities and approaches to ensure your implementations remain current and competitive.
With proper planning, execution, and ongoing optimization, your SAP implementation can deliver sustainable business value for years to come.
FAQs
How long does an SAP implementation take?
SAP implementation timelines vary significantly based on project scope, complexity, and organizational factors. For small to medium-sized businesses implementing core modules, projects typically require 6-12 months from planning to go-live. Enterprise-wide implementations for large organizations generally take 12-24 months to complete fully.
What is the difference between SAP ECC and SAP S/4HANA?
SAP ECC (ERP Central Component) and SAP S/4HANA represent different generations of SAP’s enterprise resource planning software. Specifically, SAP ECC uses a traditional database structure with separate transactional and analytical systems. In contrast, S/4HANA utilizes in-memory computing technology that dramatically improves processing speed and analytical capabilities.
What is the difference between a greenfield and brownfield SAP implementation?
Greenfield and brownfield approaches represent fundamentally different strategies for SAP implementation. In a greenfield implementation, organizations start with a clean slate, implementing SAP without carrying forward configurations or customizations from legacy systems. This approach enables full adoption of SAP best practices but requires more extensive process redesign.
What are the main risks in SAP implementation projects?
SAP implementation projects face several significant risks that can impact project success and business operations. First, scope creep represents a major threat, as expanding requirements can derail project timelines and budgets. Second, resource constraints, particularly around specialized SAP expertise, can create bottlenecks and quality issues. Third, data quality problems often emerge during migration efforts, potentially affecting system functionality and user confidence. Fourth, inadequate testing may allow critical issues to reach production, disrupting business operations.
What are the common challenges in an SAP implementation?
Common challenges in SAP implementation projects include both technical and organizational factors that can impact project outcomes. Specifically, aligning diverse stakeholder expectations often proves difficult, as different departments prioritize different requirements and timelines. Additionally, managing integration complexity between SAP and legacy systems frequently creates technical hurdles and performance issues.