The stakes couldn’t be higher, with India’s artificial intelligence market projected to reach USD 17 billion by 2027, according to Moneycontrol. Understanding AI regulations in India is about survival and success in one of the world’s fastest-growing tech ecosystems.
The landscape of AI regulations in India has crafted is both promising and challenging. Unlike the rigid frameworks emerging in other jurisdictions, India has taken a more nuanced approach, balancing innovation with responsibility.
From the landmark MeitY advisory that sent shockwaves through the startup community to the evolving principles from NITI Aayog, the regulatory environment continues to evolve at breakneck speed.
What makes this particularly challenging is that AI regulations in India encompasses isn’t just about one comprehensive law – it’s a patchwork of guidelines, advisories, existing legislation, and emerging frameworks that businesses must navigate carefully.
Whether you’re a multinational corporation or a bootstrapped startup, understanding these regulations will determine whether your AI initiatives thrive or face regulatory roadblocks that could derail years of hard work.
Current State of AI Regulation in India (2025 Overview)
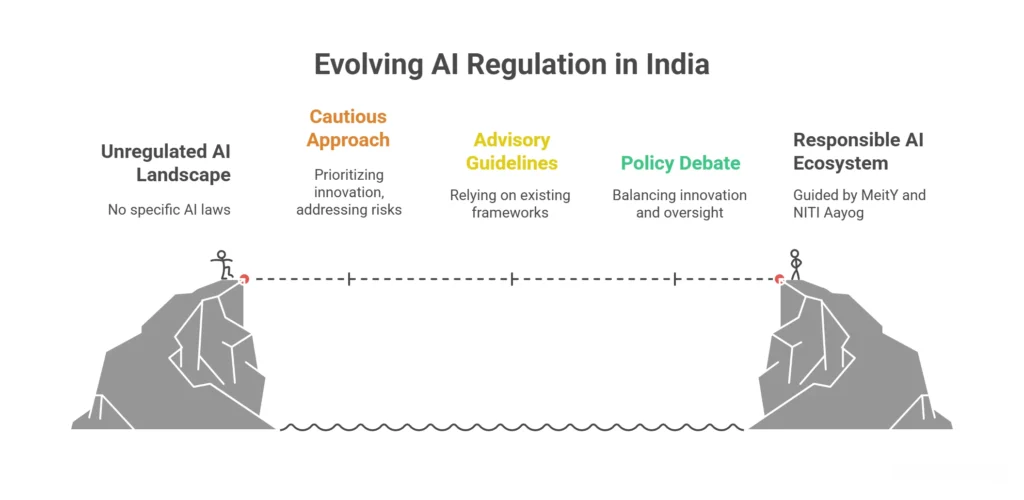
Understanding the current regulatory environment requires recognizing that AI regulations in India operates within a unique framework that prioritizes innovation while addressing emerging risks.
The government has adopted a cautious yet progressive approach, avoiding heavy-handed legislation while establishing foundational guidelines for responsible AI development.
Unlock the Power of AI, Responsibly
Stay ahead of generative AI regulations in India with expert solutions that ensure compliance while driving innovation.
Explore Generative AI ServicesNo Comprehensive AI-Specific Laws Yet
Currently, there are no specific codified laws, statutory rules, or regulations in India that directly regulate AI. This absence of dedicated legislation creates both opportunities and uncertainties for businesses operating in the AI space.
Moreover, the regulatory approach relies primarily on existing frameworks and advisory guidelines rather than comprehensive statutory requirements.
Pro-Innovation vs. Regulatory Approach Debate
The ongoing debate between fostering innovation and implementing regulatory oversight shapes AI regulation India discussions.
Furthermore, policymakers recognize that premature or excessive regulation could stifle India’s growing AI ecosystem, while inadequate oversight might expose citizens to potential risks from unregulated AI deployment.
Key Regulatory Bodies and Their Roles
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) serves as the primary regulatory authority for AI governance.
The MeitY is the apex ministry established by the central government to regulate and be responsible for the development and facilitation of the use of AI regulation India. Additionally, NITI Aayog provides strategic guidance and policy recommendations for AI development across various sectors.
Major AI Regulatory Frameworks and Guidelines
India’s regulatory approach to AI has evolved through multiple frameworks and guidelines that collectively shape the current landscape.
Correspondingly, these documents provide the foundation for understanding AI regulation India requirements and best practices for AI development and deployment in the Indian market.
NITI Aayog’s Principles for Responsible AI
NITI Aayog has established fundamental principles emphasizing transparency, accountability, and fairness in AI systems. Additionally, these principles in AI regulation India, guide developers toward creating AI solutions that serve societal needs while minimizing potential harms.
The framework emphasizes human-centric design and ethical considerations throughout the AI development lifecycle.
National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence (#AIForAll)
National Institution for Transforming India (NITI) Aayog, a central government-backed policy think tank, published the National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence in June 2018.
Moreover, this comprehensive strategy outlines India’s vision for leveraging AI across sectors, including healthcare, agriculture, education, smart cities, and transportation, while addressing potential societal challenges.
Operationalizing Principles for Responsible AI
These guidelines in AI regulation India translate high-level principles into actionable frameworks for AI developers and deployers.
The operationalization framework provides specific recommendations for risk assessment, algorithmic auditing, and ongoing monitoring of AI systems to ensure compliance with responsible AI principles.
NASSCOM Guidelines for Generative AI
The National Association of Software and Service Companies (NASSCOM) has developed industry-specific guidelines for generative AI solutions, providing practical frameworks for content generation, intellectual property rights, and the responsible deployment of large language models in commercial applications.
In addition to that, these guidelines address concerns related to content generation, intellectual property rights, and the responsible deployment of large language models in commercial applications.
The Landmark MeitY Advisory (March 2024) and Its Impact
The March 2024 MeitY advisory represents a pivotal moment in AI regulation India, establishing the first concrete compliance requirements for AI platforms and intermediaries. Thus, this advisory has significantly shaped how businesses approach AI deployment and compliance in the Indian market.
Original Advisory Requirements and Industry Pushback
The original Advisory mandated that the use of under-testing or unreliable AI models must have explicit permission from the Government of India and should be labelled appropriately for users.
Moreover, this requirement in AI regulation India faced significant industry opposition due to concerns about innovation bottlenecks and implementation challenges for startups and smaller companies.
Revised Advisory: Key Changes and Current Obligations
Following industry feedback, MeitY revised its advisory on March 15, 2024, removing the government approval requirement while maintaining core compliance obligations.
The Advisory requires all intermediaries to ensure compliance with the Advisory from immediate effect i.e., 15 March 2024, onwards. Furthermore, the revised version focuses on platform responsibilities rather than pre-deployment approvals.
Compliance Requirements for Platforms and Intermediaries
Significant social media intermediaries must implement robust content moderation systems, establish grievance redressal mechanisms, and ensure AI-generated content doesn’t violate existing AI regulation India.
Moreover, these requirements apply primarily to large platforms rather than individual developers or small startups.
Labeling and Metadata Requirements for AI-Generated Content
Platforms must implement systems to identify and label AI-generated content, particularly deepfakes and synthetic media.
Additionally, this requirement aims to enhance transparency and help users distinguish between human-created and AI-generated content, addressing concerns about misinformation and fraud.
Existing Laws Affecting AI Development and Deployment
While India lacks comprehensive AI-specific legislation, several existing laws significantly impact AI development and deployment. Understanding these intersections is crucial for ensuring compliance with the current AI regulation India.
Information Technology Act 2000 and IT Rules 2021
AI regulation India, per the IT Act 2000 and subsequent IT Rules 2021, establishes the foundational framework for digital governance in India.
Furthermore, these regulations address data protection, cybersecurity, and platform responsibilities that directly impact AI systems handling personal data or user-generated content.
Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023
The DPDP Act 2023 introduces comprehensive data protection requirements that significantly impact AI systems processing personal data.
Furthermore, AI developers must implement privacy-by-design principles and ensure compliance with consent, data minimization, and purpose limitation requirements throughout the AI lifecycle.
Intellectual Property Considerations for AI
Current IP laws in AI regulation India present complex challenges for AI-generated content and inventions. Questions regarding copyright ownership of AI-generated works, patentability of AI-invented solutions, and protection of AI algorithms remain areas of ongoing legal development and interpretation.
Sector-Specific Regulations (Banking, Healthcare, Telecom)
Financial services, healthcare, and telecommunications sectors have additional regulatory requirements that impact AI deployment. Overall, these sector-specific regulations often include data localization requirements, audit obligations, and specialized approval processes for AI-based solutions.
Upcoming Legislative Developments
The regulatory landscape for AI regulation India continues evolving with several significant legislative developments expected in 2025 and beyond. Additionally, these upcoming changes will likely provide greater clarity and comprehensive frameworks for AI governance.
Draft Digital India Act 2023 and AI Provisions
The proposed Digital India Act aims to replace the Information Technology Act 2000 with a more comprehensive framework addressing modern digital challenges.
Expected AI provisions include algorithmic accountability requirements, platform liability frameworks, and enhanced user protection mechanisms.
Proposed AI Governance Guidelines Report (February 2025)
NITI Aayog is expected to release comprehensive AI regulation India guidelines in February 2025, providing detailed frameworks for AI risk assessment, regulatory compliance, and industry-specific applications.
Overall, these guidelines will likely influence future legislative developments and industry best practices.
AI Safety Institute Initiative
The government is exploring establishing an AI Safety Institute to provide technical expertise, conduct research on the risks of generative AI, and develop safety standards for AI systems. This institute would play a crucial role in shaping future AI regulation India policies, and international collaboration efforts.
Expected Timeline for Comprehensive AI Legislation
Industry experts anticipate comprehensive AI legislation within the next 2-3 years, likely following the publication of NITI Aayog’s governance guidelines and public consultation processes. Moreover, the timeline depends on political priorities, industry feedback, and international regulatory developments.
Industry-Specific AI Regulatory Considerations
Different sectors face varying levels of regulatory scrutiny and compliance requirements for AI implementation. Additionally, understanding these sector-specific considerations under AI regulation India is essential for businesses operating in regulated industries.
Financial Services and RBI Guidelines
The Reserve Bank of India has issued guidelines for AI adoption in banking and financial services, emphasizing risk management, algorithmic auditing, and customer protection.
Correspondingly, these guidelines, per AI regulation India, require banks to implement robust governance frameworks and ensure explainable AI systems for critical decisions.
Healthcare AI and Regulatory Oversight
Healthcare AI applications face additional scrutiny from medical device regulations, patient data protection requirements, and clinical trial obligations.
Furthermore, the regulatory framework emphasizes safety, efficacy, and ethical considerations for AI systems used in diagnostic and treatment applications.
Telecommunications Sector AI Regulations
Telecom operators using AI for network optimization, customer service, and fraud detection must comply with TRAI regulations and data localization requirements.
Additionally, this AI regulation India addresses spectrum management, consumer protection, and national security considerations related to AI deployment.
E-commerce and Consumer Protection
E-commerce platforms using AI for recommendations, pricing, and customer service must comply with consumer protection laws and platform liability requirements. Finally, these regulations address fair trade practices, data transparency, and dispute resolution mechanisms for AI-driven decisions.
Compliance Requirements for Businesses in 2025
Navigating AI regulation India compliance requires understanding specific obligations that apply to different types of generative AI, businesses, and AI applications. Moreover, these requirements vary based on company size, sector, and AI use cases.
Due Diligence Obligations for AI Platforms
AI platforms must conduct thorough due diligence on their AI systems, including risk assessments, bias testing, and impact evaluations. Finally, this includes documenting AI decision-making processes and ensuring appropriate human oversight for critical applications.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Companies must implement comprehensive risk assessment frameworks that identify potential harms from AI systems and develop appropriate mitigation strategies.
Ultimately, these assessments under AI regulation India should address bias, privacy, security, and societal impact considerations throughout the AI lifecycle.
Documentation and Reporting Requirements
Maintaining detailed documentation of AI development processes, testing procedures, and deployment decisions is essential for compliance.
In addition to that, some sectors require regular reporting to regulatory authorities of AI regulation India, about AI system performance and risk mitigation measures.
Deepfake Detection and Prevention Mandates
Platforms must implement technical measures to detect and prevent the spread of deepfakes and other harmful synthetic content. Additionally, this includes developing automated detection systems and establishing processes for user reporting and content removal.
Global Context: How India Compares to Other Jurisdictions
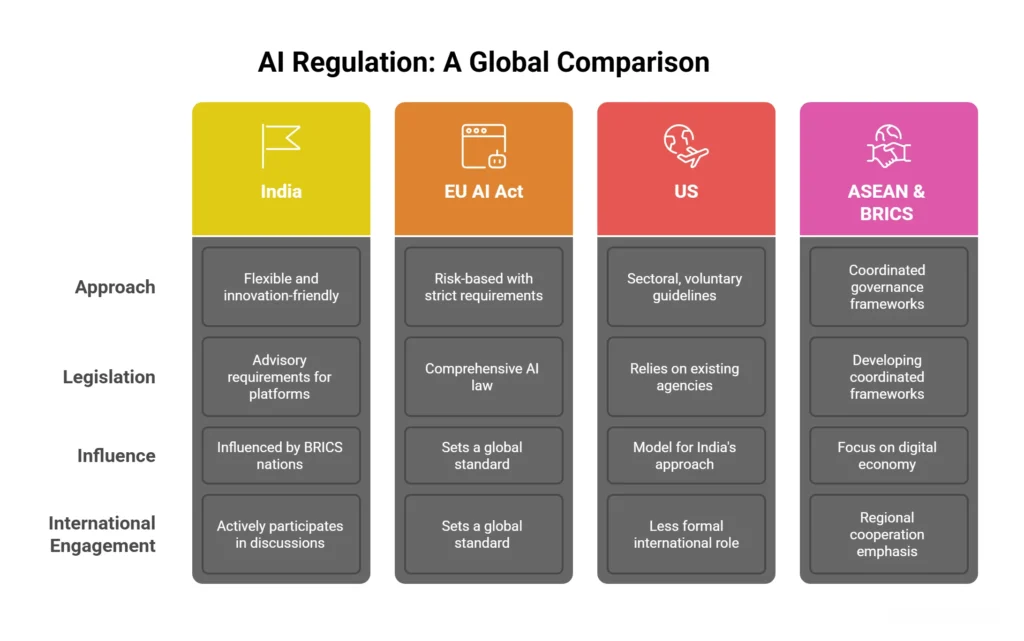
Understanding India’s position in the global regulatory landscape helps contextualize current approaches and anticipate future developments. Furthermore, India’s approach reflects its unique economic, technological, and social considerations.
India vs. EU AI Act Approach
The EU’s Artificial Intelligence Act (the “EU AI Act”) came into force on August 1, 2024. The world’s first comprehensive AI law, the EU AI Act, assumes a risk-based approach with strict requirements for high-risk AI systems.
Ultimately, this approach to AI regulation India, is more flexible and innovation-friendly, avoiding the EU’s prescriptive regulatory framework.
Comparison with the US AI Regulation Framework
The United States has adopted a sectoral approach to AI regulation, relying on existing agencies and voluntary guidelines rather than comprehensive legislation. Thus, India’s approach shares similarities with the US model but includes more specific advisory requirements for platforms and intermediaries.
ASEAN and BRICS Country Approaches
ASEAN countries are developing coordinated AI governance frameworks, emphasizing digital economy growth and regional cooperation. Moreover, BRICS nations are exploring collaborative approaches to AI governance that balance innovation promotion with risk management, influencing India’s policy development.
International Cooperation and Standards Alignment
India actively participates in international AI governance discussions through the G20, the UN, and other multilateral forums. Additionally, this engagement influences domestic policy development and ensures alignment with global best practices and standards.
Practical Steps for AI Compliance in India
Implementing effective compliance strategies requires systematic approaches that address both current requirements and anticipated future developments. Moreover, these practical steps help businesses navigate AI regulation India successfully.
Conducting AI Risk Assessments
Develop comprehensive risk assessment frameworks that evaluate potential harms from AI systems across technical, ethical, and societal dimensions. In addition, regular assessments should inform ongoing system improvements and compliance strategies.
Implementing Responsible AI Frameworks
Establish organizational policies and procedures that embed responsible AI principles throughout the development lifecycle. This AI regulation India includes ethics review processes, bias testing protocols, and stakeholder engagement mechanisms.
Building Compliance Documentation
Maintain detailed records of AI development processes, testing results, and deployment decisions. Proper documentation supports regulatory compliance and helps demonstrate due diligence in case of audits or investigations.
Training and Capacity Building Requirements
Invest in training programs that ensure teams understand AI regulations in India requirements and best practices. Furthermore, this includes technical training on compliance tools and processes as well as awareness programs for non-technical stakeholders.
Future Outlook: What to Expect Beyond 2025
The evolution of AI regulations in India will likely accelerate as technology advances and regulatory frameworks mature. Understanding emerging trends helps businesses prepare for future compliance requirements and opportunities.
Anticipated Regulatory Developments
Expect more detailed sectoral guidelines, enhanced enforcement mechanisms, and greater international alignment in AI governance approaches.
Ultimately, the AI regulations in India framework will likely become more sophisticated as policymakers gain experience with AI governance challenges.
Industry Self-Regulation Trends
Industry associations are developing voluntary standards and best practices that may become foundations for future regulatory requirements. Self-regulation initiatives help shape policy development and demonstrate industry commitment to responsible AI development.
International Harmonization Efforts
Growing international cooperation on AI governance will likely influence India’s regulatory approach. In addition to that, harmonization efforts aim to reduce compliance burdens for global companies while maintaining appropriate protections for citizens.
Emerging AI Technologies and Regulatory Challenges
New AI technologies like artificial general intelligence, quantum machine learning, and brain-computer interfaces will present novel regulatory challenges. Policymakers must balance innovation promotion with appropriate risk management for emerging technologies.
Conclusion
The journey through AI regulations in India in 2025 isn’t just about compliance; it’s about participating in the creation of frameworks that will shape how artificial intelligence develops and serves society for generations to come.
Your understanding of these regulatory requirements doesn’t just protect your business from compliance risks; it positions you as a responsible innovator in India’s growing AI ecosystem.
The companies that thrive in this environment will be those that view AI regulations in India not as a burden, but as a foundation for building trust with users, investors, and society at large.
At American Chase, we specialize in helping businesses understand and comply with evolving AI regulations.
Our expert team can guide you through the complexities of AI regulation India, ensuring your innovations reach the market while meeting all compliance requirements.
Contact us today to learn how we can support your AI compliance journey and help your business thrive in India’s regulated AI environment.
Harness AI Innovation While Navigating Regulations
Partner with us to implement generative AI solutions that comply with evolving regulations and maximize business impact.
Talk to AI ExpertsFrequently Asked Questions
1. Does India have specific laws regulating artificial intelligence in 2025?
No, India currently lacks comprehensive AI-specific legislation. AI regulation India relies on existing laws, guidelines, and advisories from various regulatory bodies, while comprehensive legislation remains under development.
2. What are the key requirements of the March 2024 MeitY advisory on AI?
The advisory requires intermediaries to ensure AI systems don’t enable unlawful content sharing, implement proper labeling for AI-generated content, and obtain government approval for unreliable AI models under AI regulation India framework.
3. Do startups need government approval before deploying AI models in India?
Under current AI regulation India guidelines, only intermediaries and platforms require government approval for deploying unreliable or under-testing AI models. Individual startups developing AI solutions generally don’t require pre-approval.
4. What are the penalties for non-compliance with India’s AI guidelines?
Current AI regulation India penalties vary by applicable law, ranging from monetary fines under IT Rules to potential blocking of services. Specific penalties depend on violation severity and applicable regulatory framework.
5. How does the Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023 affect AI development?
The DPDP Act significantly impacts AI development by regulating personal data processing, automated decision-making, and consent mechanisms, creating additional compliance requirements under AI regulation India framework for data-driven AI systems.
6. What labeling requirements exist for AI-generated content in India?
AI regulation India requires clear labeling of AI-generated content indicating potential inaccuracies or unreliability. Platforms must implement consent mechanisms informing users about AI-generated content and its limitations.
7. Which sectors have specific AI regulatory requirements in India?
Banking, healthcare, telecommunications, and e-commerce sectors have specific AI regulatory requirements under AI regulation India framework, with each sector having tailored guidelines addressing unique risks and use cases.
8. How does India’s AI regulations approach compare to the EU AI Act?
Unlike the EU’s comprehensive risk-based legislation, AI regulation India emphasizes principles-based guidance and industry self-regulation, offering more flexibility while maintaining a responsible development focus.
9. What is the role of NITI Aayog in AI governance in India?
NITI Aayog develops foundational AI principles and national strategy documents that guide AI regulation India policy development, providing frameworks for responsible AI development and deployment across sectors.
10. When can we expect comprehensive AI legislation to be enacted in India?
Industry experts anticipate comprehensive AI legislation under AI regulation India framework by late 2025 or early 2026, following public consultation completion and alignment with international standards.