Talk to any IT leader today, and SAP is likely part of that conversation, but not in the way it used to be. What once sat quietly in the background, handling transactions and operations, is now at the center of digital transformation agendas. The future of SAP is being carved out by how quickly organizations adapt it to solve modern challenges.
In 2025, it’s no longer about whether to modernize SAP, but how fast you can do it without breaking things. From manufacturing floors to finance teams, businesses are asking more from their systems, and SAP, in many ways, is answering.
Not with promises, but with actual shifts in:
- How data is used,
- How workflows are designed, and
- How intelligence is embedded into everyday decisions.
So, this blog cuts through the buzz and focuses on what’s actually changing. We’ll understand the future of SAP, walk through the latest trends, and SAP artificial intelligence trends that are shaping SAP’s trajectory.
If you’re building with SAP or building for it, this is the landscape you’re stepping into.
Current State of SAP in the Enterprise Landscape
Before we dive into the future of SAP, it’s important to understand where things stand today. SAP has never been a static player, it has shifted alongside business priorities, technology shifts, and user demands.
SAP’s Market Position and Global Adoption
SAP continues to hold a critical position in the enterprise technology space. Over 400,000 businesses across the globe rely on its systems to run core functions like
- Finance,
- Supply chain,
- HR,
- Manufacturing, and
- More.
Whether it’s Fortune 100 giants or mid-sized firms scaling up operations, SAP often sits at the heart of digital infrastructure.
Moreover, adoption trends show that industries are not just maintaining their SAP environments, they’re investing in new capabilities. From SAP S/4HANA migrations to cloud-first deployments, the future of SAP is ever expanding.
Evolution from Traditional ERP to Intelligent Enterprise
Over the past decade, SAP has quietly transitioned from a traditional ERP system to something far more dynamic. As discussed earlier, what used to be a transactional engine has now evolved into a digital foundation built for intelligent enterprise scenarios.
Several layers of innovation like real-time data processing, SAP cloud transformation, and embedded machine learning have driven this transformation.
Furthermore, the future of SAP is clearly evolving toward systems that respond proactively, predict outcomes, stay connected, and adapt to context. While that may sound ambitious, much of this future is already unfolding.
Businesses are gradually shifting from reactive reporting to forward-looking decision support systems, all built into the SAP ecosystem.
Key Challenges Facing SAP Users Today
Despite strong capabilities and a bright future of sap, the adoption isn’t always smooth. One major friction point is complexity, customizations built years ago often create roadblocks during modernization. Moreover, many organizations also struggle with fragmented data landscapes, where integrations across tools and platforms lack consistency.
Cost and skills are another concern. SAP implementations require deep domain knowledge, and finding talent that understands both legacy environments and modern modules can be a hurdle.
Then there’s change fatigue. For teams that have been through multiple transformation cycles, yet another upgrade or migration often meets resistance.
That’s where expert SAP development and consulting becomes essential. Remember, it’s not about deploying faster, it’s about aligning tools with actual business goals, without overloading teams or budgets.
AI and Machine Learning Integration in SAP
The future of SAP is AI, and the move toward intelligence is already well underway. But what makes 2025 stand out is the scale at which artificial intelligence is being built directly into the architecture.
Instead of functioning as an optional add-on, AI is becoming a default layer, woven across modules, business logic, and user interfaces.
SAP’s AI Strategy and Technology Stack
SAP is not following the AI trend, it’s engineering its own roadmap. From embedded machine learning within SAP S/4HANA to the Business Technology Platform’s (BTP) AI Core services, the ecosystem is built to scale intelligence without overcomplicating deployments.
At the center of this approach is a focus on outcome-driven use cases, process optimization, data enrichment, and fraud detection. For enterprises building toward the future of SAP, understanding this evolving AI stack is essential to staying competitive.
Predictive Analytics and Intelligent Automation
Secondly, it has now grown to be able to anticipate what happens next. SAP predictive analytics solutions are giving finance, sales, and logistics teams the power to act before problems arise.
Moreover, coupled with intelligent automation, these tools help streamline decisions, eliminate repetitive tasks, and reduce dependencies on manual processes. As a result, businesses using these tools wisely are saving time and spotting opportunities faster.
Natural Language Processing and Conversational Interfaces
User experience inside SAP is getting an overdue upgrade, thankfully. Through NLP capabilities and conversational AI, employees can now interact with SAP systems using voice or simple text commands. Whether it’s checking inventory levels or generating a custom report, the interface feels intuitive.
And as the future of SAP pushes toward autonomy, these AI-driven interactions will replace countless screens and clicks with direct, human-like engagement. The goal is clear, let the system speak your language, not the other way around.
Real-World AI Applications in SAP Modules
The future of SAP and AI together is no longer limited to labs and pilot programs, it’s already solving real problems. In SAP Ariba, algorithms help predict supplier risk. In SAP SuccessFactors, machine learning suggests better talent matches during recruitment. SAP IBP (Integrated Business Planning) now uses AI to simulate demand shifts with accuracy.
Thus, SAP automation and AI integration show how reliable they are in shaping decisions across industries. Businesses tapping into these capabilities are moving closer to systems that act like strategic partners, not just software tools.
Emerging Technologies Shaping the Future of SAP
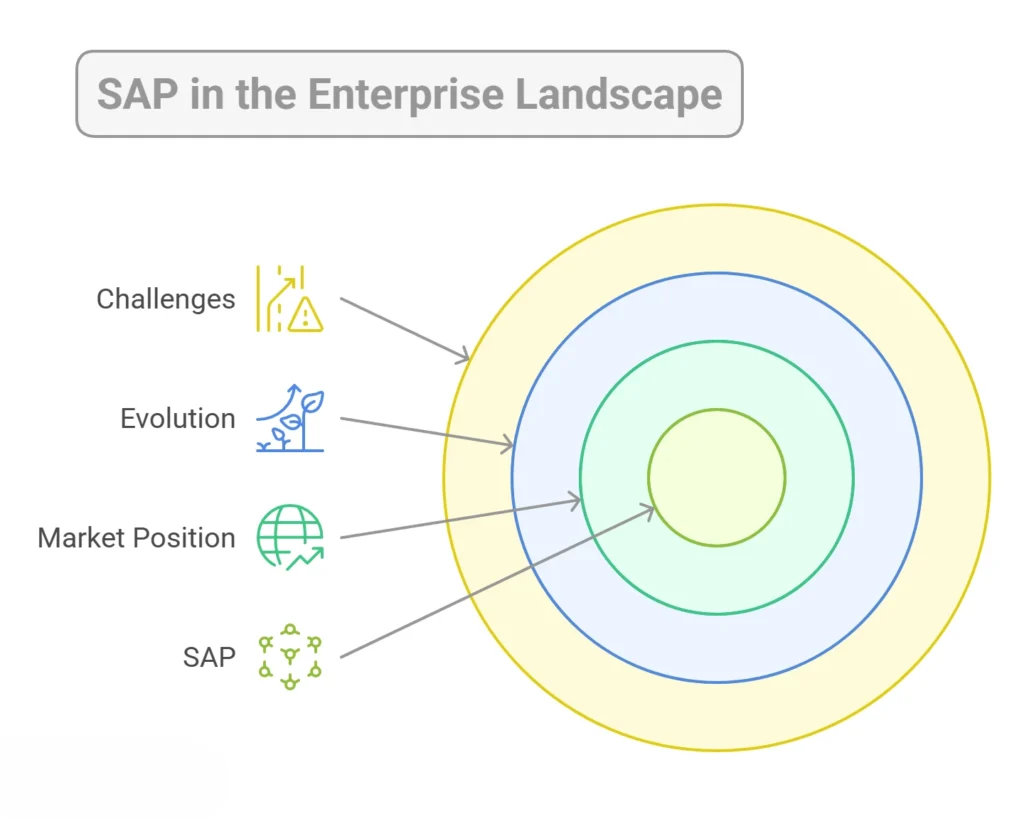
As digital ecosystems expand, SAP is anticipating what’s next. A new generation of technologies is finding its place within the SAP universe, and they’re beginning to solve complex, real-world problems in elegant ways. Here’s what the future of SAP will look like:
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The physical and digital worlds are blending, and IoT is making that connection seamless. SAP is using IoT to bring machine data, environmental inputs, and real-time sensor feedback directly into business operations.
In manufacturing, this means predictive maintenance and downtime avoidance. Moreover, in logistics, it enables dynamic route optimization based on actual traffic or weather conditions.
So, by embedding IoT insights into the future of SAP systems, companies may gain the agility to act immediately rather than after the fact.
Blockchain Technology in Supply Chain Management
Blockchain in SAP is also becoming a powerful layer for trust and traceability. In supply chain scenarios, it offers an unalterable ledger that tracks every movement, transaction, and checkpoint.
This visibility is essential in industries like pharma, food, and electronics, where provenance and compliance are critical. Furthermore, SAP’s integration of blockchain helps eliminate fraud, reduce paperwork, and build partner trust.
As the future of SAP unfolds, this technology may redefine how enterprise agreements, shipments, and audits are handled end-to-end.
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality Applications
AR and VR are also the future of SAP. They are no longer limited to gaming, they’re beginning to reshape how enterprise users experience data and processes. In the SAP ecosystem, AR can project real-time system data onto physical assets. Think of maintenance engineers viewing machine health overlaid on actual equipment.
VR, on the other hand, can immerse new hires in simulated training environments built with live SAP workflows. Thus, these experiences solve onboarding, safety, and operational challenges with powerful visualization.
Edge Computing and Real-Time Processing
Cloud isn’t the only answer, sometimes, data decisions need to happen at the edge. SAP’s expanding focus on edge computing is helping businesses process information where it’s generated, on factory floors, inside trucks, or at field sites.
As a result, this reduces latency and improves responsiveness, especially in mission-critical use cases like asset monitoring, energy management, or production control.
The future of SAP will be shaped by how effectively enterprises balance central cloud processing with decentralisation, and SAP is already building the tools to do exactly that.
Challenges and Considerations for SAP’s Future
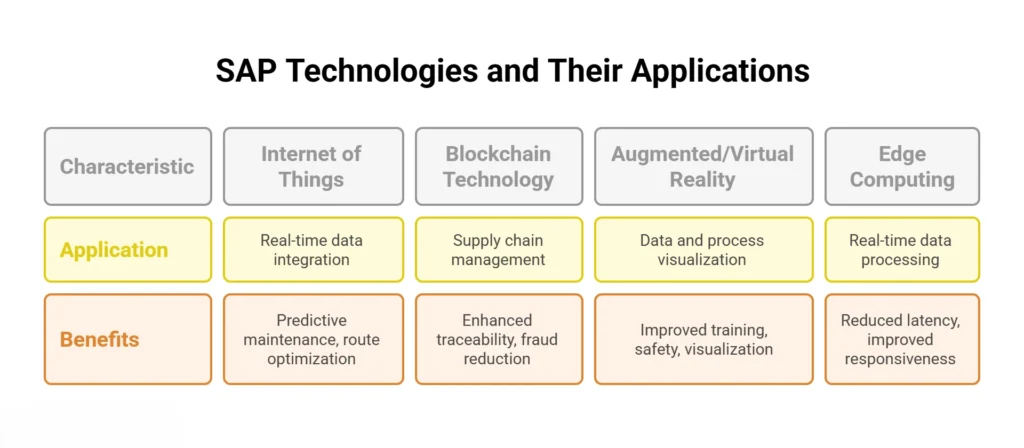
Every major shift comes with friction. As SAP technologies become more advanced, many organizations face a new kind of complexity. So before learning about the future of SAP, it’s crucial to pause and look at what’s practical.
Legacy System Integration and Technical Debt
One of the core blockers in the future of SAP journey is legacy infrastructure. Companies that have heavily customized their systems over the years often find themselves tangled in outdated code, manual dependencies, or rigid architectures.
Therefore, integrating new tools with these older environments is also strategic. Rewriting isn’t always feasible, but neither is standing still. Finding balance is key.
Data Privacy and Regulatory Compliance
In a hyperconnected world, data governance is not a checkbox, it’s a moving target. SAP systems, particularly those operating across borders, must stay aligned with regional and industry-specific compliance frameworks.
GDPR, HIPAA, and others continue to evolve. So, the future of SAP must account for how data is stored, moved, accessed, and deleted, without creating friction in operations. In short, building privacy by design into configurations is quickly becoming non-negotiable.
Cost Management and ROI Optimization
Transitioning to SAP S/4HANA or adopting AI features often comes with a high upfront cost, and that’s where doubts creep in. Stakeholders want to see returns, but measuring ROI from complex implementations isn’t always straightforward. Budgets tighten. Expectations rise.
That’s why the future of SAP should have cost management embedded in every decision, from license models to integration timelines. Also, tracking value at each milestone keeps both technical and business teams aligned.
Change Management and User Adoption
No matter how powerful the platform, change won’t stick unless people embrace it. SAP’s transformation touches day-to-day workflows, which means resistance is natural. Furthermore, long-time users may push back, and new users may feel overwhelmed.
Communication, phased rollouts, and in-context training matter more than most teams realize. Also, building trust in the system is something that will shape the future of SAP.
To navigate these challenges well, businesses are now seeking comprehensive SAP implementation strategies that don’t just solve today’s problems but are flexible enough to support tomorrow’s growth.
The Future of SAP: Predictions for SAP in 2025 and Beyond
Now that we’ve covered what’s working and what’s holding things back, it’s time to look ahead. SAP in 2025 is about convergence. As multiple technologies mature together, the possibilities stretch far beyond just process automation or digitization.
Here’s what’s likely to define the future of SAP.
Next-Generation ERP and Business Applications
Traditional ERP systems focused on recording transactions. The next generation will center around intelligence like predicting demand, suggesting actions, and offering real-time insights without needing constant user input.
Additionally, these systems will likely adapt to user roles and behavior patterns over time. The future of SAP will not revolve around only dashboards, but decisions will be made faster and delivered within workflows, not outside them.
Autonomous Enterprise and Self-Healing Systems
Imagine a setup where your SAP landscape detects an error, corrects it, and notifies the right team, all without manual interference. That’s not science fiction, that’s the future of SAP. Autonomous systems are gradually making their way into enterprise IT.
From auto-scaling cloud environments to self-tuning processes, this shift will redefine how support, maintenance, and operations are handled in the years ahead.
Sustainability and Green IT Initiatives
Environmental accountability is becoming a serious boardroom agenda. So, SAP has started embedding sustainability metrics into its core tools. These include: energy tracking, emission reporting, and lifecycle management across supply chains.
But this is only the beginning. The future of SAP may include carbon-aware procurement modules, eco-based routing in logistics, and AI-driven recommendations to reduce resource consumption.
Global Market Expansion and Emerging Markets
Lastly, as we know, new markets are rising fast, like Africa, Southeast Asia, parts of Eastern Europe, and SAP is paying attention. While the software stack remains global, implementations must adapt to local regulations, currencies, languages, and infrastructure realities.
Cloud adoption in these regions is giving SAP an edge in scalability and speed. At the same time, industry-specific solutions are being tailored to smaller but fast-growing businesses.
Conclusion: The Future of SAP
To be precise, the future of SAP is no longer limited to IT roadmaps, it’s now a critical part of how companies define agility, resilience, and long-term value.
With AI integration and real-time intelligence becoming the norm, SAP is shifting from being a system of record to a platform of foresight.
Yet, transformation doesn’t happen in isolation. It requires strategy, alignment, and the right partnerships. Whether you’re modernizing legacy environments or exploring intelligent automation, navigating this evolution takes clarity and precision.
If your organization is preparing to step into the next era of enterprise technology, it may be the right time to contact American Chase and explore what’s possible with a focused, execution-first mindset.
Looking ahead, the future of SAP will belong to those who build with intent, bridging innovation with impact, and turning complexity into opportunity.
FAQs about the Future of SAP
1. What are the key technologies shaping the future of SAP development?
A set of emerging technologies is actively guiding SAP’s evolution, moving far beyond traditional ERP thinking. Developers are building artificial intelligence directly into core modules, while machine learning strengthens forecasting and decision-making. Meanwhile, cloud-native development is replacing rigid, on-premise architectures.
2. How is SAP S/4HANA different from traditional SAP ERP systems?
S/4HANA is a complete shift in design philosophy. Unlike older systems that relied on batch processing and heavy customization, S/4HANA operates in real time, supports in-memory computing, and prioritizes simplicity in both UX and data models. It also integrates AI-driven insights and predictive tools natively. Thus, S/4HANA is the future of SAP.
3. How is AI being integrated into SAP applications?
AI is now baked into the SAP architecture, not just layered on top. From automating invoice approvals in finance to recommending candidates in recruitment modules, machine learning is working behind the scenes to reduce manual input and boost speed.
4. What should organizations consider when planning for SAP’s future?
It starts with understanding the gap between where your systems are now and where they need to be. Organizations must assess infrastructure readiness, talent capabilities, and internal appetite for change. Also, security, scalability, and long-term support models deserve a close look.