You might have the most feature-rich Java web application, but if it lags, users will leave. Speed is nowadays an expectation. In fact, according to a Google study, a one-second delay in page load time can reduce conversions by 20%. That’s why performance optimization in Java web application development is mission-critical, not optional.
Java, as we all know, remains a top choice for enterprise-grade web apps. But poor tuning, memory leaks, inefficient code, and database latency can quickly erode user experience. The good news?
Optimizing performance doesn’t have to be overwhelming. From profiling tools to JVM tuning, this blog breaks down 10 techniques of performance optimization in Java web applications that can significantly enhance speed and reliability.
Let’s dive into the playbook because faster apps mean better outcomes for your users and your bottom line.
Why Java Web App Performance Optimization Matters
Before implementing fixes, it’s important to understand why performance matters so much in Java-based systems. From improving user satisfaction to keeping operational costs under control, performance optimization in Java web application projects can directly impact business outcomes.
-> User experience, business outcomes, and operational costs
A fast, responsive interface is no longer a nice-to-have, it’s expected. Delays or poor performance drive users away and reduce engagement. Performance optimization in Java web application development ensures a seamless experience, boosting customer satisfaction and lifetime value. The better your app performs, the less support it needs and the more conversions it can achieve.
Moreover, sluggish applications also increase cloud hosting costs and hurt scalability. Over time, these inefficiencies translate into wasted resources and revenue loss. That’s why performance must be a priority from the start of the web development life cycle to deployment and beyond.
-> Common performance bottlenecks in Java web apps
Even the most well-written applications can suffer from performance issues if bottlenecks aren’t addressed. Frequent culprits include large object creation, inefficient data structures, poor database queries, and thread contention. Each of these issues compounds latency, making responsiveness unpredictable.
So, focusing on performance optimization in Java web application architecture allows teams to identify root causes and mitigate them systematically. Also, without proactive monitoring and analysis, these problems can remain hidden until they cause user churn or server instability.
10 Proven Techniques for Performance Optimization in Java Web Application
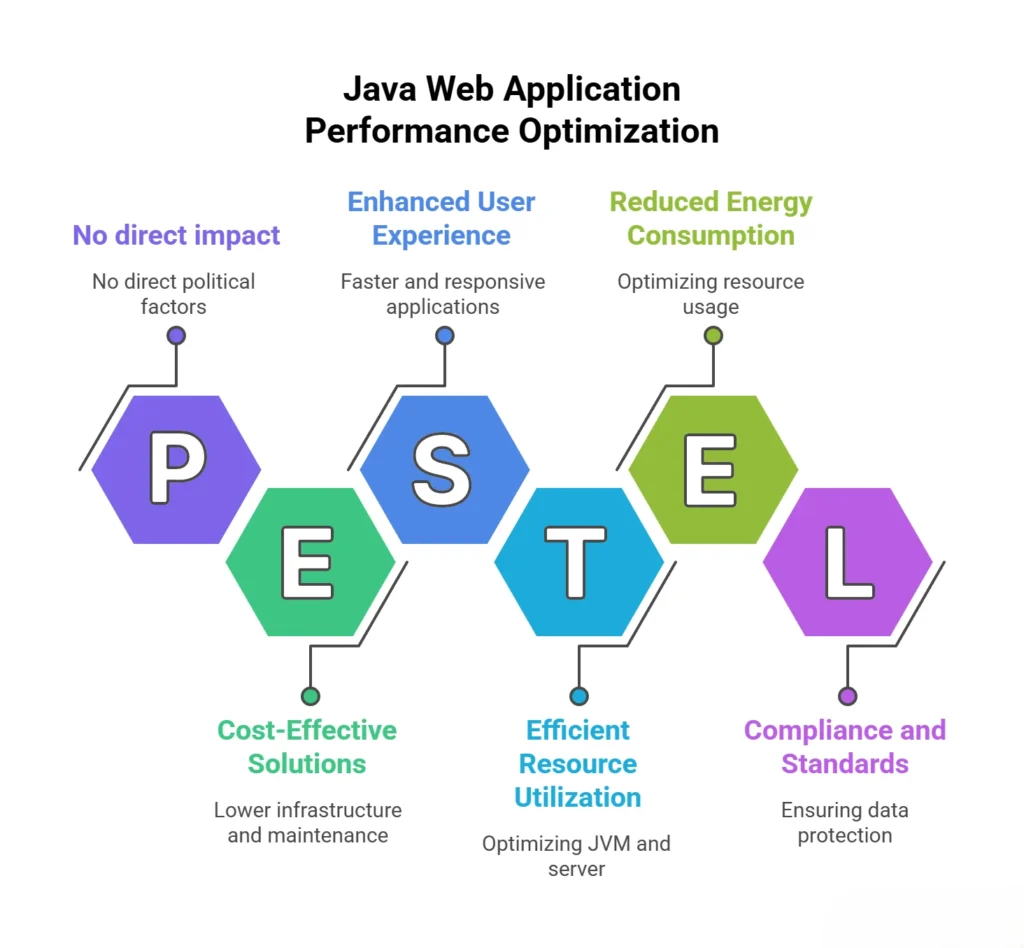
When it comes to delivering fast, scalable, and responsive digital experiences, performance optimization in Java web application development is non-negotiable. From streamlining backend logic to minimizing latency and tuning JVM settings, there are several ways developers can boost efficiency.
Below, we explore ten tried-and-tested techniques that can help you fine-tune your application for peak performance.
1. Profiling and Identifying Bottlenecks
Before jumping into code-level fixes, it’s essential to first understand where your Java application is slowing down. This step lays the foundation for effective performance optimization in Java web application projects by helping you target the most impactful areas for improvement.
-> Using Java Profiling Tools (VisualVM, JProfiler, Java Flight Recorder)
Profiling tools are indispensable for identifying runtime inefficiencies. Tools like VisualVM, JProfiler, and Java Flight Recorder allow you to inspect memory consumption, CPU usage, garbage collection activity, and more. As a result, this visibility makes it easier to pinpoint which parts of the app require tuning.
-> Analyzing CPU, Memory, and Thread Usage
Once you’ve gathered performance data, the next step is interpreting it. High CPU usage may signal algorithmic inefficiencies, while thread contention often hints at poor concurrency management. Interpreting these signs correctly helps prioritize fixes that yield the most improvement.
2. Code and Algorithm Efficiency
Even with the best infrastructure, inefficient code can quickly drag down performance. Improving algorithmic logic and reducing unnecessary computations are core strategies for performance optimization in Java web application development.
Especially when working on scalable, custom web development projects where flexibility can sometimes lead to over-engineered solutions.
-> Choosing the Right Data Structures and Algorithms
Selecting appropriate data structures like HashMaps over Lists or Sets for search-heavy operations can drastically reduce execution time. The same applies to choosing sorting algorithms or handling recursive logic, small changes here compound significantly at scale.
-> Refactoring Long Methods and Optimizing Loops
Breaking down long methods improves readability and can help isolate performance bottlenecks. Similarly, optimizing loops, such as reducing nested iterations or moving invariant computations outside the loop, can yield major gains.
3. Efficient Memory and Garbage Collection Management
Memory handling can make or break the responsiveness of a Java web application. Mismanaged memory not only increases latency but can also lead to crashes under load. Moreover, with the rise of cloud and DevOps integration, scalable apps need consistent and predictable garbage collection behavior.
-> Java Memory Model Overview
Understanding the Java memory model is essential for diagnosing memory leaks and optimizing resource use. Also, knowing how heap, stack, and metaspace are utilized helps in tailoring memory allocation strategies for smoother performance optimization in Java web application builds.
-> Tuning Garbage Collection for Web Apps
Choose the right GC algorithm (G1, ZGC, or CMS) depending on your application’s throughput and latency requirements. Tuning GC parameters like pause time goals and thread counts can drastically reduce lag during high-traffic periods.
4. Optimizing Database Operations
Databases often become the primary bottleneck in performance optimization in Java web application projects. Inefficient queries, lack of indexing, and excessive round-trips can slow down even the most optimized code. Therefore, addressing database design early is crucial for long-term scalability and efficiency.
-> Using Indexes, Joins, and Batch Processing
Indexes speed up queries, especially on large datasets, while well-structured joins improve data retrieval without redundancy. Batch processing is also a go-to technique for reducing overhead when performing repetitive inserts or updates.
-> Reducing Network Round-Trips and ORM Pitfalls
Minimize how often your application calls the database by consolidating queries and avoiding N+1 problems common in ORM frameworks. These small changes go a long way in driving performance optimization in Java web application development.
5. String and Object Handling Best Practices
Inefficient string operations and excessive object creation can silently degrade performance. Java developers must be intentional about how they manage memory and reuse objects, especially in high-traffic web environments.
-> StringBuilder vs Concatenation
Using StringBuilder instead of the + operator in loops or frequent modifications avoids the overhead of creating multiple immutable string objects. It’s one of the simplest ways to achieve better performance optimization in Java web application backends.
-> Minimizing Object Creation and Reusing Resources
Avoid creating new instances when existing ones can be reused safely. Utilize object pools where possible, especially for expensive resources like database connections or HTTP clients, to maintain consistent throughput and memory efficiency.
6. Multi-threading and Concurrency
Scalability in Java web applications often hinges on how well concurrency is managed. Therefore, leveraging multi-threading properly allows apps to handle numerous simultaneous users without degrading performance.
-> Thread Pools and Executor Services
Creating new threads for every task is costly. Thread pools and Java’s ExecutorService offer more efficient task management. Thus, reducing latency and supporting better performance optimization in Java web application architecture. This technique ensures that system resources are used optimally without overwhelming the server.
-> Synchronization Best Practices
Overusing synchronization can cause thread contention and slowdowns. Apply it only when necessary and consider using java.util.concurrent utilities to achieve thread-safe operations with minimal performance trade-offs.
7. Caching Strategies in Java Web Apps
Caching is one of the most powerful yet underutilized techniques of performance optimization in Java web application. It reduces load times and database queries in Java web applications. A smart caching strategy can dramatically improve the user experience while lowering infrastructure costs.
-> Application-level caching (Ehcache, Redis)
Implement in-memory caches like Ehcache or Redis to store frequently accessed data such as product lists, user profiles, or config values. These tools allow developers to cache responses at the service or controller level, significantly minimizing repeated data fetching and boosting overall throughput.
-> Memoization and result caching
Memoization stores method results in memory, avoiding repeated calculations. This technique of performance optimization in Java web application is useful for methods that are computation-heavy but return predictable results. Moreover, combined with proper cache invalidation logic, it helps balance performance and consistency.
8. Front-end and Network Optimization
Before diving into backend systems, optimizing the front-end and network layers of a Java web application development project can deliver instant performance gains. These optimizations improve load times, reduce server strain, and directly impact user experience.
-> Minimizing HTTP requests, optimizing static resources
Reducing the number of HTTP requests by combining CSS/JS files and leveraging image sprites can significantly cut load times. Additionally, optimizing static resources like images through lazy loading and compression helps deliver faster, leaner web pages.
-> GZIP compression and CDN usage
GZIP compression can shrink the size of transferred files by up to 70%, speeding up communication between client and server. Pair this with a CDN to distribute content globally and reduce latency. During large-scale deployments or architectural changes, it’s important to ensure this performance optimization in Java web application is preserved through careful planning and testing.
9. JVM and Server Configuration Tuning
Java applications rely heavily on the JVM’s internal configuration to run smoothly under varying workloads. Tuning the JVM and server settings can eliminate performance bottlenecks and ensure better stability and scalability in production environments.
-> Heap Size, Thread Settings, and Connection Pooling
Before tweaking your code, you must ensure your Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and server are configured for optimal performance. The heap size determines how much memory your application can use. Too little and you risk frequent garbage collection, too much and you may hit system limits.
-> Choosing the Right JVM Options for Your Workload
Selecting the right JVM options can significantly impact performance optimization in Java web application development. Parameters such as -Xms, -Xmx, -XX:+UseG1GC, and thread stack size need careful calibration depending on your application’s workload pattern. So, fine-tuning these settings ensures balanced memory use, avoids performance cliffs, and supports consistent throughput during peak loads.
10. Continuous Performance Testing and Monitoring
A one-time speed boost is not enough. For consistent performance optimization in Java web application projects, continuous testing and real-time monitoring are crucial. By integrating these into CI/CD workflows, teams can catch regressions early and respond before users are affected. This practice transforms performance from a reactive task into a proactive culture.
-> Load Testing Tools and Metrics
To maintain application reliability, regularly running load tests with tools like JMeter, Gatling, or Locust is essential. These tools help simulate realistic traffic and identify performance bottlenecks under stress. Also, monitor key metrics such as latency, throughput, error rate, and resource utilization.
-> Building a Performance Culture in Development Teams
Creating a performance-first mindset across development teams is just as important as having the right tools. Encourage developers to write efficient code, review performance in pull requests, and prioritize testing for scalability. When performance goals are shared, measurable, and integrated into every sprint, teams can deliver faster, more stable Java applications every time.
Conclusion: Performance Optimization in Java Web Application
Navigating the path to performance optimization in Java web application development is not just about fine-tuning code or tweaking server settings. It’s a continuous process that spans architecture decisions, tooling, testing, and fostering the right development culture.
From leveraging serverless advantages to JVM tuning and real-time monitoring, every layer contributes to delivering fast, reliable digital experiences.
If you’re looking to build scalable, high-performance web applications with expert guidance, partner with American Chase, your trusted ally in building robust, future-ready digital solutions.
FAQs about Performance Optimization in Java Web Application
1. What are the essential tools for profiling Java web application performance?
Some essential profiling tools include VisualVM, JProfiler, and Java Mission Control. These help detect memory leaks, CPU bottlenecks, and thread contention issues. Thus, making it easier to maintain optimal application speed.
2. How can garbage collection tuning speed up my Java web app?
Proper GC tuning minimizes pause times and ensures efficient memory management. Tools like G1GC and ZGC can significantly improve Java application optimization by balancing throughput and responsiveness.
3. What database optimization techniques work best for Java applications?
Use connection pooling, indexing, and query caching. Also, tools like Hibernate Profiler and SQL monitoring help detect slow queries, enabling backend performance optimization.
4. How do I choose between multi-threading and asynchronous processing for web apps?
It depends on your workload. For I/O-bound operations, asynchronous processing is ideal, while multi-threading works well for CPU-bound tasks. Combining both can help you strike the right performance balance in modern Java web applications.
5. What are the most common code-level mistakes that slow down Java web applications?
Inefficient loops, excessive object creation, and blocking I/O calls are major culprits. Identifying and refactoring such issues is a crucial step in performance optimization in Java web application development.
6. How often should I review and update my performance optimization strategies?
Ideally, after every major release or architectural change. Continuous profiling and regular testing help keep Java server performance in check and prevent regressions over time.
7. What role does caching play in boosting web application speed?
Caching reduces the load on both the database and the server by storing frequently accessed data. Implementing local and distributed caching layers like Redis or Ehcache is central to performance optimization in Java web application architecture.